Information in the review is provided as of February 1, 2023
Summary.
Active combat training in the Belarusian Armed Forces continued in January. The combat readiness of some units was inspected during the month. The experience of the war in Ukraine was actively used in combat training.
The level of military presence of the Russian Armed Forces didn’t change in January. There may be about 2000 servicemen of the Russian Armed Forces in Belarus. The activity of units of the Russian Armed Forces deployed in Belarus is very low.
The number of PMC Wagner mercenaries in Belarus may still amount to several hundred people. Training of representatives of military structures by mercenaries continues. We can note the intensification of cooperation between PMC Wagner and the Belarusian Armed Forces.
The general medium-term forecast of the military situation in Belarus remains the same: there is no reason to expect an offensive by the Russian Armed Forces from the territory of Belarus, as well as an increase in their military presence. The Belarusian Armed Forces joining the war on the side of Russia is also not an obvious factor. The significance of PMC Wagner as a destabilizing factor has almost disappeared.
1. Armed Forces of the Republic of Belarus. Internal Troops.
1.1. Organization of combat training.
In January, combat readiness inspections were conducted in the Belarusian Armed Forces. The inspections were conducted in the 30th Railway Brigade, the 52nd Separate Tank Battalion of the 6th Mechanized Brigade, the 339th Separate Mechanized Battalion of the 120th Mechanized Brigade, the 111th Artillery Brigade, etc. Combat readiness inspections were conducted both at the units’ permanent deployment points and at training grounds.
There were also reports of inspections of the on-duty units of the rapid reaction forces of the 6th and 11th Mechanized Brigades. These are units of permanent readiness, which will first and foremost fulfill their assigned tasks. Also, at the end of January, the 1st Separate Mechanized Battalion of the 19th Mechanized Brigade, as well as one of the mechanized battalions of the 11th Mechanized Brigade, were brought to readiness to complete training and combat tasks. As part of the inspection, these units went to training grounds to conduct drills.
Inspections were also conducted of the on-duty forces of the Air Force and Air Defense Forces, including units of the 15th Anti-Aircraft Missile Brigade. Drills were also conducted with units of the anti-aircraft missile and radio-technical troops, as well as aviation.
The start of field drills with units of the 350th Artillery Group was also reported.
Important combat training activities include the following:
1) Snipers of reconnaissance and special purpose units of the Western Operational Command have been trained at the training center of the 103rd Airborne Brigade for a month. Personnel were trained in terrain orientation, camouflage of shooting positions, tactics of operations in a sniper pair and overcoming mine and explosive barriers.
2) A training session for UAV operators was held in the 51st Artillery Brigade. During the training, servicemen improved FPV drone piloting techniques on a simulator, as well as ammunition dropping with the use of UAVs.
3) On January 9-11, a training session for battalion (divizion) commanders and their deputies was held in the Western Operational Command. The purpose of the training session was to improve the effectiveness of combat training in the units, taking into account the experience of the war in Ukraine. During the training, they focused on learning how to conduct combat operations in winter conditions. Particular attention was paid to solo training and the level of readiness of servicemen to conduct combat operations both autonomously and as part of small units. The issues of non-standard use of military equipment available to the Western Operational Command were also considered.
4) On January 23-26, a joint staff training was held at the command posts of the Belarusian Armed Forces under the leadership of the Chief of the General Staff. During the training, the issues of planning the use of troops in accordance with the training situation, which was developed taking into account the forecast of the situation development on the European continent, were practiced. Representatives of military commissariats of Minsk region, the Internal Affairs and Emergency Situations bodies, and the Internal Troops took part in the training. Such trainings are conducted regularly.
5) On January 15, a group of Belarusian military went to Russia for training. There were representatives of the operational commands of the Ground Forces and the Special Operations Forces among the servicemen. The training is held at the 333rd combat training center of the Western Military District of the Russian Armed Forces and will last for a month. The training will focus on the experience gained by the Russian Armed Forces during the war in Ukraine. After the training is completed, the Belarusian military will share their experience with units of the Belarusian Armed Forces as instructors. In fact, the Belarusian Armed Forces are changing their approach to the organization of combat training and have started to establish an institute of professional instructors. For more details, see the brief of 30.01.2024 “The Belarusian Armed Forces are establishing an institute of instructors and changing the approach to the organization of combat training”.
The presence of units of the Special Operations Forces of the Belarusian Armed Forces in the regions of Belarus bordering Ukraine continues. According to our information, units of the 103rd Airborne Brigade and the 5th Special Purpose Brigade are involved in these activities. Despite the fact that it is officially declared that the military are performing tasks to protect the border with Ukraine, in reality, they are also guarding Russian military facilities in Homiel region.
Training of servicemen by PMC Wagner mercenaries continued. As before, more active training was conducted with the Internal Troops. There were reports of mercenaries training with the Tornado special purpose detachment and the beginning of a new training course for servicemen of special purpose units of the Internal Troops.
There were also reports of trainings with the Belarusian Armed Forces. For example, Wagner mercenaries started training the 202nd Separate Mechanized Battalion of the 6th Mechanized Brigade. During the training, they practice trench fighting, evacuation of the wounded, assault and defense of buildings. The beginning of training of a battalion of the 6th Mechanized Brigade by Wagner mercenaries may indicate a change of paradigm, when the mercenaries were training mainly servicemen of the Internal Troops. Joint training of mercenaries with other mechanized units of the Belarusian Armed Forces can be expected in the near future.
1.2. Movements of military equipment and aviation activity.
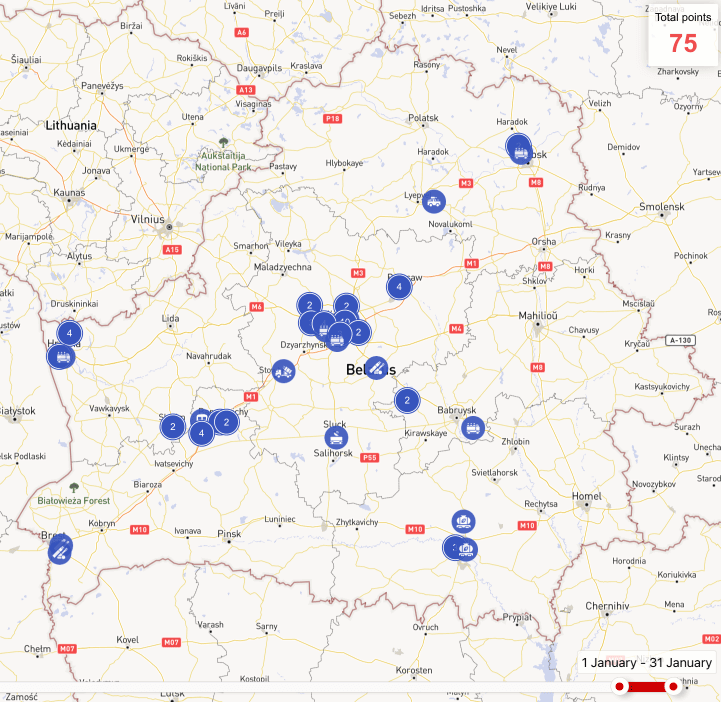
The intensity of movements of military equipment remained almost the same as in December. The movements were mainly related to combat training, including combat readiness inspections (for more details, see paragraph 1.1 of the review).
As in previous months, there was nothing unusual in movements of the equipment of the Belarusian Armed Forces. Most of the movements are concentrated in the vicinity of the areas where the garrisons of the Belarusian Armed Forces are deployed. Therefore, the information spread by the Ukrainian mass media about the alleged gathering of military equipment at the Belarusian-Ukrainian border is not confirmed. Most likely, these reports were part of an informational provocation.
More details on the movements of military equipment are available on the map of military activity.
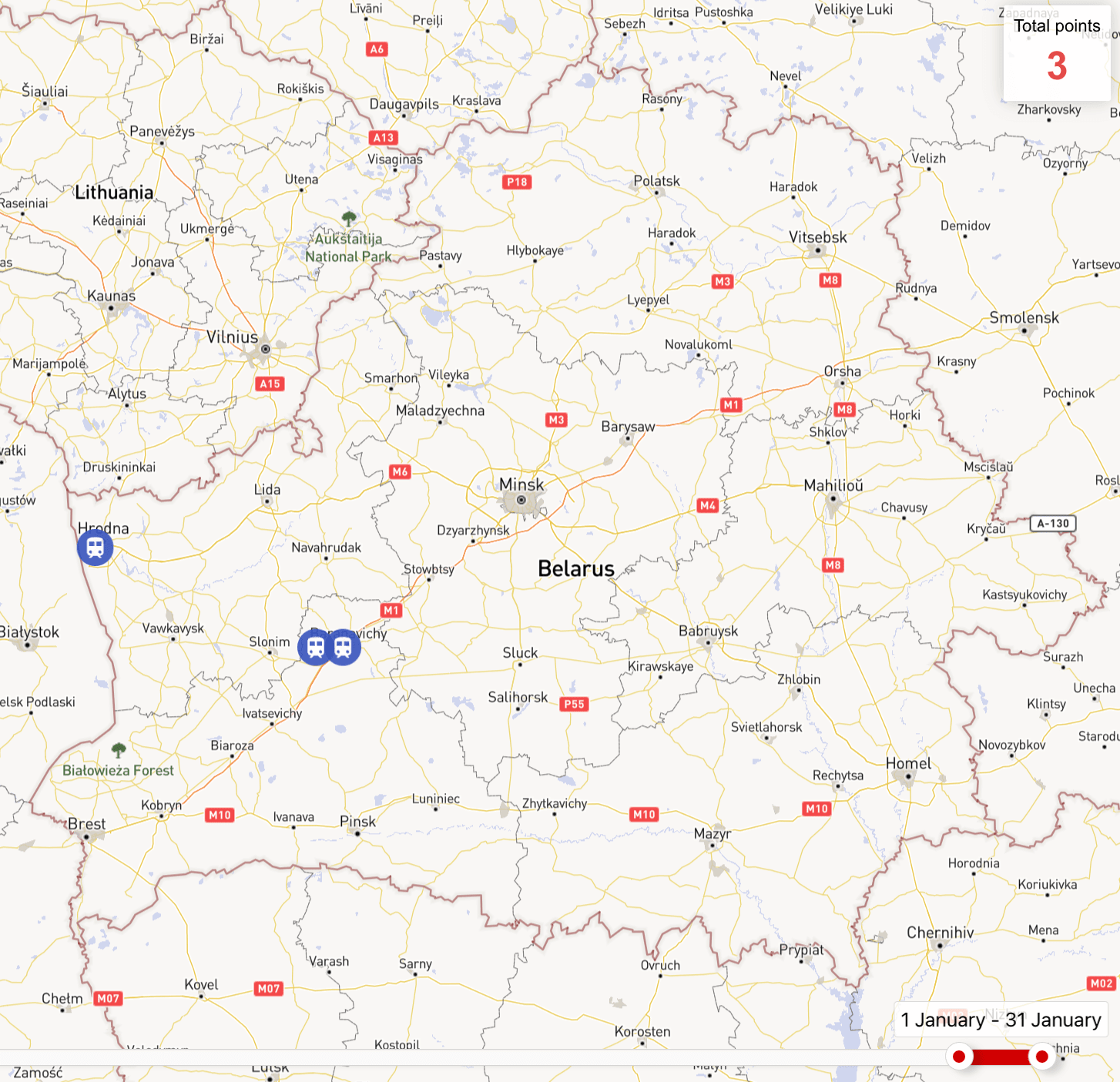
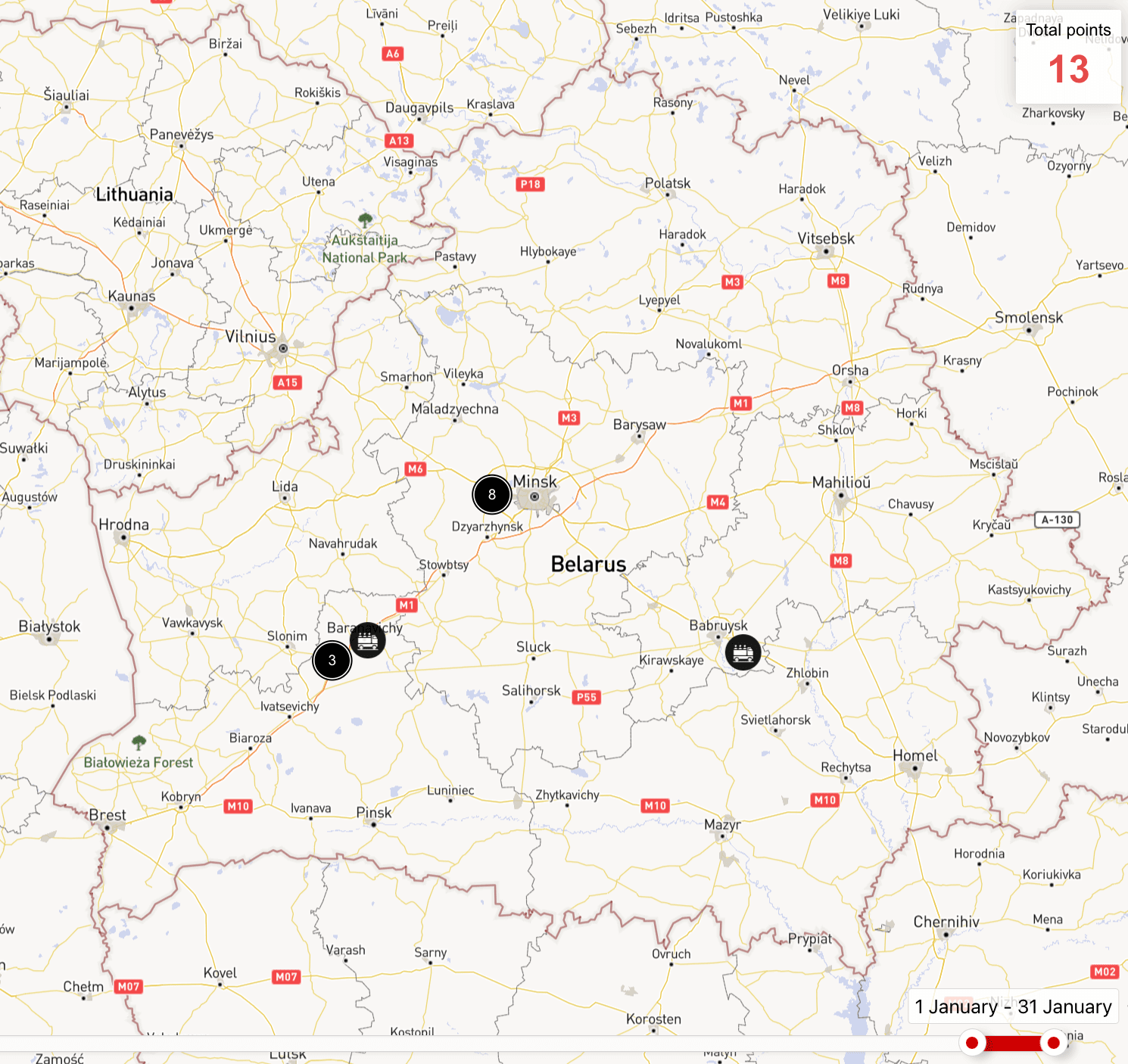
The intensity of movements of the Belarusian Armed Forces by rail remained at the same level as in December. Only one military cargo train with equipment of the 6th Mechanized Brigade was recorded in January (for more details, see paragraph 1.1 of the review).
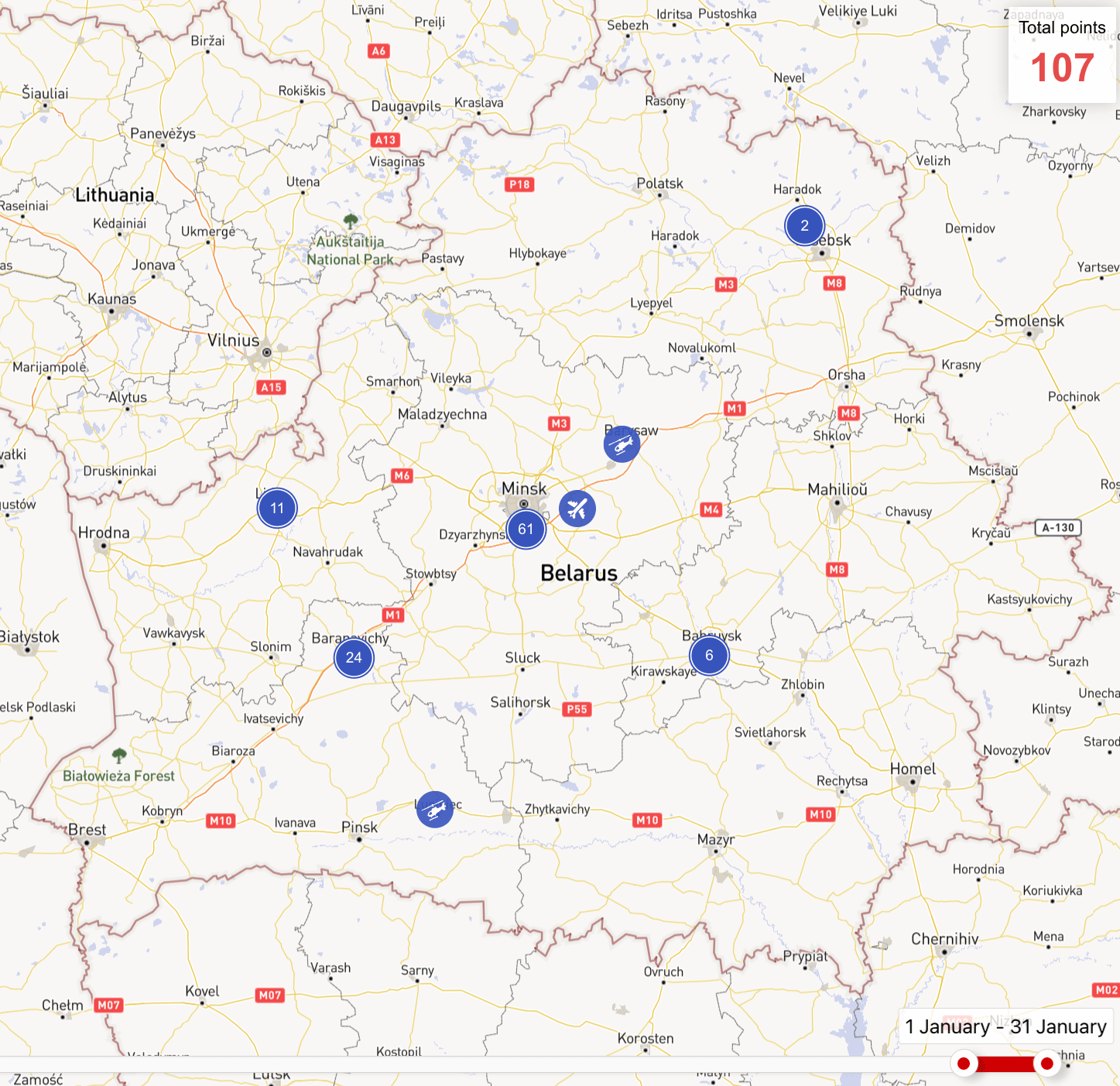
The intensity of flights of the Belarusian Air Force remained at the same level as in December. Lida, Baranavichy and Machulishchy airfields were mainly used for flights, while Luninets and Babruisk airfields were used less frequently. The entire helicopter and aircraft fleet of the Belarusian Air Force was involved in the flights.
Nothing unusual was observed during the flights. We would only note that during the month, flights of aircraft and helicopters of the Belarusian Air Force in the area of the borders with Poland and Ukraine were recorded.
1.3. Military commissariats. Territorial defense and national home guard.
During the month, military commissariats conducted trainings with reserve officers assigned to the territorial troops, administrations of mobilization facilities, headquarters for notification of reservists, and others. It was also reported that trainings on military transportation duties, military registration and reservation of persons liable for military service were held.
No drills with the territorial defense and national home guard were reported in January. The nearest such drills should be expected in March.
Other notable events include the following:
1) On January 5, the 5th Militia Brigade of the Internal Troops held firearms training with the chairmen of district executive committees of Mahiliou region. It was noted that the experience gained from the mercenaries of PMC Wagner was used during the training.
2) On January 17, the Chief of the General Staff met with the Chairman of the Hrodna Regional Executive Committee. At the meeting, they discussed the improvement of the security of Belarus’ borders on the territory of Hrodna region and the introduction of advanced military experience in the practice of training territorial troops, including the equipment and organization of fortified areas. Most likely, at the meeting they discussed the construction of a new facility of ‘Khrenin’s line’ on the territory of the region (for more details, see paragraph 1.5 of the review).
3) In January-February, local budgets for 2024 are traditionally published. The available information allows us to conclude that the trend of increasing expenditures of local budgets on national defense continues. The full picture of expenditures can be seen in March, when all documents are published.
In January, only 3 court verdicts were reported in criminal cases against citizens who evaded conscription for active military service (Article 435 of the Criminal Code). This is not a final figure yet, as sentences are published in the public domain with a delay.
1.4. Military training sessions with reservists.
During the month, it was reported that about 40 reservists were drafted to military training sessions by military commissariats of Minsk and Brest regions. At the same time, there is no data on the number of reservists drafted from Hrodna, Homiel, Vitsiebsk and Mahiliou regions. Therefore, in reality, about 120 reservists (≈20 people from each region) could have been drafted to the training session. Other conscriptions of reservists for military training sessions were not reported.
The Ministry of Defense of Belarus didn’t report on the number of reservists planned to be drafted to military training sessions in 2024. According to the plans for 2023, a total of 9000 people were planned to be drafted to training sessions. However, the declared limit was exceeded in May 2023.
We shouldn’t expect the intensity of military training sessions to decrease in 2024. This is indicated by the changes in the rules for military training sessions, which allow for more frequent conscription of reservists.
1.5. Rearmament and activity of the military-industrial complex. Development of military infrastructure. Formation of new units.
Supplies of new military equipment and ammunition to the troops.
There were reports on the supplies of new military equipment to the Belarusian Armed Forces in January.
1) Reconnaissance and special purpose units of Western Operational Command received Russian-made TAYGA PATRUL 551 SWT snowmobiles. The number of snowmobiles purchased was not specified.
2) UAV aviation detachments of the 6th and 11th Mechanized Brigades received new simulators to conduct training with multi-rotor UAV and FPV drones operators.
Plans on rearmament were announced:
1) On January 11, servicemen of the Belarusian Armed Forces went to Russia for training on the Krasukha-S4 EW system. It was noted that the Krasukha-S4 system would be delivered to the Belarusian troops in the second half of 2024. Most likely, the equipment will enter service with the 48th Separate Electronic Warfare Battalion (military unit 97061) stationed in Brest.
2) Units of the Western Operational Command are to receive a new batch of DJI Mavic 3 quadcopter-type UAVs soon. The terms of delivery of quadcopters were not announced. It was noted that their number was planned to provide each motorized rifle, reconnaissance and artillery unit with UAVs. In 2022, the Ministry of Defense of Belarus purchased about 100 DJI Mavic 2 and DJI Mavic 3 quadcopters.
3) The Deputy Commander of the Air Force and Air Defense Forces of Belarus said, “In the foreseeable future, we will finish updating the fleet of our fighter aircraft, because the MiG-29 aircraft is approaching the point when [its] resources will be exhausted.” Earlier, it was reported that the Belarusian Air Force would receive a new batch of Russian Su-30SM fighters in 2023, but the delivery never took place.
We should also note that in December 2023, two rail cars with small arms ammunition were delivered from Russia. The cargo was delivered to Halynets station (Mahiliou district), near which the 2783rd base of storage and utilization of armored equipment (military unit 63615) is located. In total, about 4-4.5 million of 7.62×39 mm caliber or 8.5-9 million pieces of 5.45×39 mm caliber could have been delivered to Belarus. The recipient of the ammunition is unknown. And in early January, the Chinese Air China Cargo airline made four cargo flights in a row from Urumqi to Minsk National Airport. Everything indicates that military cargoes could have been delivered to Belarus.
Activity of the military-industrial complex.
1) Modernization of the 12.7 mm. NSVT tank machine guns is being conducted at the 815th technical support center to provide the tank crew with the ability to fire the machine gun outside the combat vehicle. It was also reported on the modernization of the 12.7 mm Degtyarev-Shpagin large-caliber machine gun for bipod firing.
2) Mechanized units of the Belarusian Armed Forces continue to adopt the experience of the war in Ukraine and manufacture anti-drone canopies equipped with the Contact-1 dynamic protection. The canopies are manufactured by repair units of mechanized brigades, the 815th technical support center, and are designed to protect armored vehicles from kamikaze drones, FPV drones, and missiles of anti-tank systems.
Development of military infrastructure.
Work on the establishment of fortified areas along the border will continue. This was stated by the head of the Main Department of Combat Training of the Belarusian Armed Forces on January 16. According to the official, this year a fortified area will be established in Hrodna region. It was noted that “deeply echeloned defense is being built on the main road directions or probable directions of enemy’s actions.” Last year, similar objects were built in Homiel and Brest regions. The media call these fortifications ‘Khrenin’s line’.
Formation of new units.
The formation of a maneuvering group of 300 people was completed in the Mazyr border guard detachment. The group is the main reserve of the border guard detachment, which is used at the border in case of escalation of the situation. The maneuvering group was armed with the Volat V1 armored vehicles and the 30-mm AGS-17 Plamya automatic grenade launchers. The establishment of maneuver groups was first announced in 2018.
1.6. Tactical nuclear weapons.
A number of events related to the deployment of TNWs in Belarus took place during the month.
1) The media, citing The Wall Street Journal, spread information that Russian TNWs could have been deployed at Lida airfield. This assumption was based on the information that one of the carriers of TNWs to be deployed in Belarus is the Su-25 attack aircraft. The aircraft are in service with the 116th Assault Air Base located in Lida. Therefore, according to the authors of the publication, TNWs could have been deployed in Lida. No other facts were given in the article.
Another TNW carrier operated by the Belarusian Armed Forces is the Iskander-M missile system. The missile system is in service with the 465th Missile Brigade stationed in Asipovichy. However, the possibility of deploying TNWs in the vicinity of Asipovichy was not reported in the media.
2) The mass media spread information about changes in the diet of Belarusian servicemen. It was about an alleged letter of the head of the logistics service of the 116th Assault Air Base to the higher command. According to the document, in order to improve the quality of nutrition of a certain category of servicemen, the following were asked to be introduced into the ration: milk and fermented milk products, fresh fruits and jam from them, an additional portion of fish, sea cabbage, condensed milk, cocoa. All changes must be approved by mid-February 2024. The information above was interpreted as indirect confirmation of TNW deployment in Lida.
The information given above may be a part of an informational provocation. This is indicated by the time of appearance of the information (a week after the publication of The Wall Street Journal) and the following facts:
1) The Instruction on peacetime food provision for the Belarusian Armed Forces (approved by Decree of the Ministry of Defense No.47 of September 13, 2004) mentioned above is no longer in force: the document was abolished in 2013. The Decree of the Minister of Defense of December 28, 2017, No.1945 “On food supply of the Armed Forces in peacetime” is now in force. The latter document could not be found in open sources. However, it is mentioned in the state procurement of food products for the Belarusian Armed Forces.
2) Some food items have already been included in the ration earlier. For example, the 2004 Instruction (referred to in the information above), which is no longer in force, included cow’s milk and fermented milk products, condensed milk (general military and flight food supply standards) and others.
Currently, there is still no reliable data that would confirm the presence of TNWs on the territory of Belarus. And all political statements about TNWs in Belarus made by Lukashenka, his officials and ‘experts’ can’t be trusted.
1.7. Amendments to legislation in the military sphere.
1) In December 2023, the Instruction on the procedure for issuing weapons and ammunition to national home guard units and keeping their records was approved. The document became publicly available in January 2024. According to the regulations of the instruction, executive committees must inform the Ministry of Defense of Belarus through military commissariats about the required number of weapons and ammunition for the national home guard.
2) On January 16, a meeting of the Security Council was held to consider the drafts of the National Security Concept and the Military Doctrine of Belarus. Both documents will be improved and subsequently approved by the All-Belarusian People’s Assembly. The previous version of the Military Doctrine was approved in 2016, and the National Security Concept– in 2010. One of the amendments to the Military Doctrine was the use of Russian tactical nuclear weapons deployed in Belarus. On January 19, Defense Minister Viktar Khrenin held a briefing on the adoption of the new Military Doctrine. According to the official, “The deployment of tactical nuclear weapons on the territory of Belarus is considered as an important component of preventive deterrence of potential enemies from unleashing armed aggression against Belarus.”
3) On January 23, decisions on the defense of the state border by border guard bodies and in the airspace in 2024 were approved. It was noted that in 2024, the construction of new border infrastructure facilities would continue, as well as the arming of maneuvering groups with modern equipment. These documents are approved annually.
1.8. International cooperation.
1) A Belarusian military delegation took part in the UMEX-2024 and SimTEX-2024 international UAV exhibitions, which were held in Abu Dhabi on January 22-25. The members of the delegation got acquainted with the latest equipment and advanced solutions in the field of unmanned aviation, and also took part in the conference on the development of unmanned systems in the defense sector. In addition, the Belarusian Belspetsvneshtekhnika and JSC KB Radar took part in UMEX-2024 as exhibitors this year.
2) On January 27, the Belarusian Defense Minister went on an official visit to Cuba. The Belarusian military delegation also included the head of the logistics of the Belarusian Armed Forces, the head of the Department of International Military Cooperation, the deputy commander of the Air Force and Air Defense Forces, the head of the General Staff Faculty of the Military Academy, and others. During the visit, negotiations were held with the Cuban Minister of Defense, which resulted in the signing of documents on bilateral military cooperation.
2. Armed Forces of the Russian Federation
2.1. Russian group in Belarus.
The situation with the group of the Russian Armed Forces in Belarus didn’t change in January compared to previous months. There is no reason to believe that servicemen of the Russian Armed Forces will start arriving in Belarus in the near future. At the same time, it is possible that if a new wave of mobilization is announced in Russia, the infrastructure of the Belarusian Armed Forces will again be used to train the mobilized.
Russian military continue to be stationed at Mazyr (Bokau) and Ziabrauka airfields. There is no information about the changes in the number of equipment located at Mazyr (Bokau) airfield at our disposal. So far, it has not been publicly reported in what status the Russian military are present at the airfields and what exactly they are doing there. Units of the 1530th Anti-Aircraft Missile Regiment of the Eastern Military District of the Russian Armed Forces (military unit 31458) are stationed at Mazyr (Bokau) airfield.
Thus, as of February 1, 2024, the number of Russian military personnel stationed in Belarus didn’t change and can be estimated at about 2000 people. Of these:
- at Baranavichy, Mazyr (Bokau) and Ziabrauka airfields – 500-600 people;
- at the Baranavichy radar station and the 43rd Vileika communication center – up to 1450 people.
2.2. Movements of military equipment and aviation activity.
The intensity of movements of military equipment on public roads has remained almost the same as in December. Only occasional movements of equipment of the Russian Armed Forces have been recorded in the vicinity of Mazyr, Homiel and Baranavichy, where the Russian military are stationed (for more details, see paragraph 2.1 of the review).
More details on the movements of military equipment are available on the map.
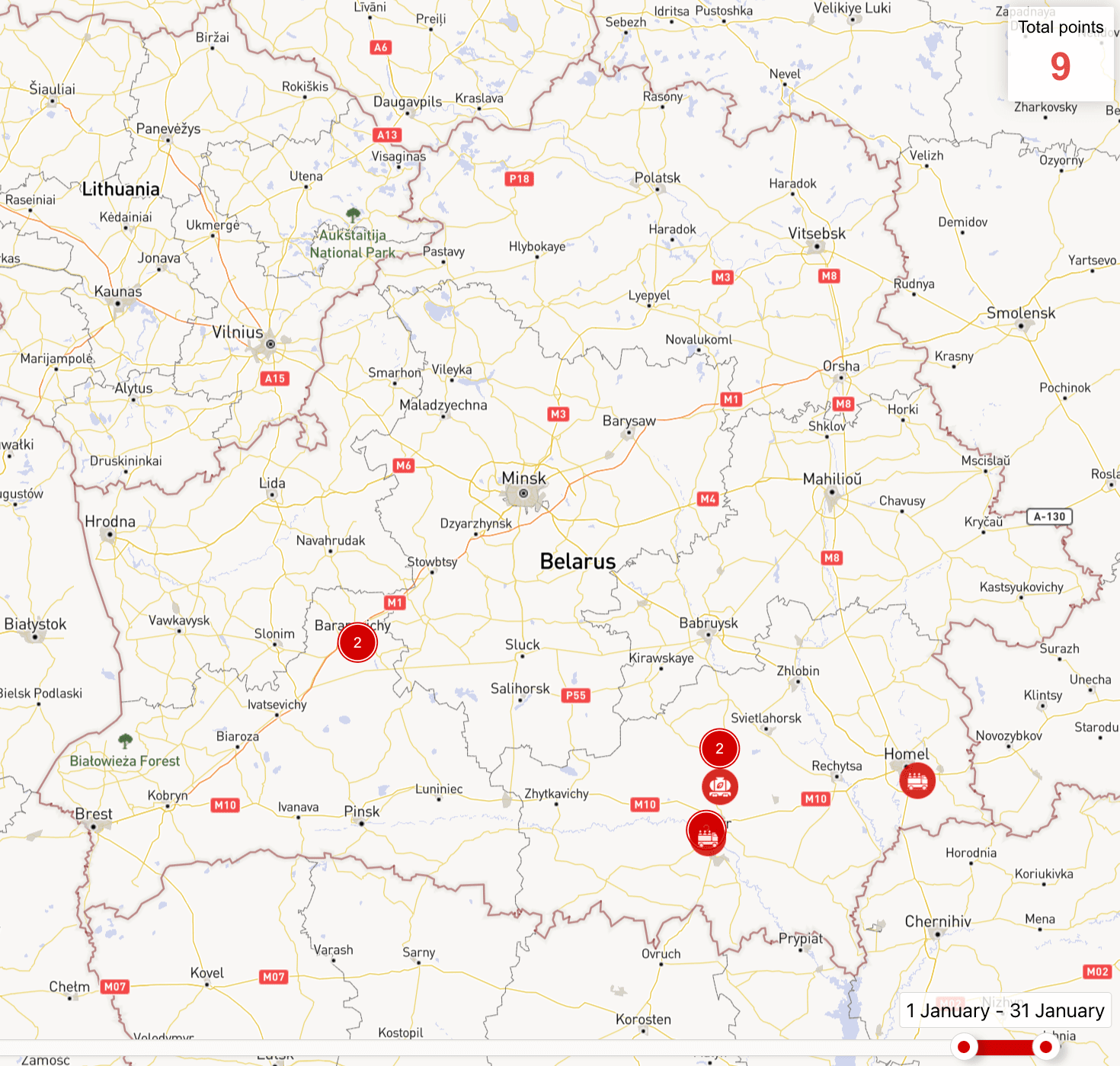
No movements of the Russian Armed Forces by rail were recorded in January. However, a freight train carrying two MZKT-543M chassis was recorded. The vehicles were new and were probably on their way to a customer in Russia. The MZKT-543M chassis are used as a wheeled base for the Tornado-S MLRS and S-400 Triumf SAM systems.
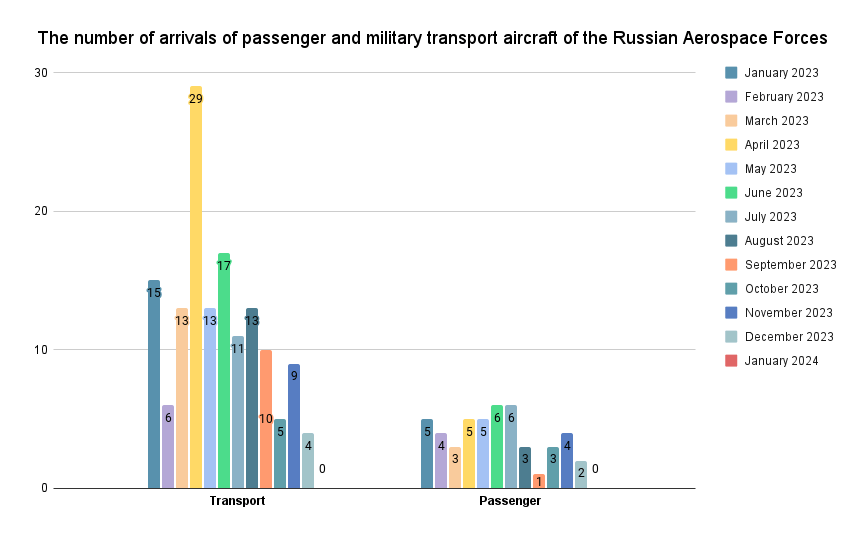
Aviation activity of the Russian Aerospace Forces significantly decreased in January compared to December. For instance, for the first time since February 2022, no military transport and passenger aircraft of the Russian Aerospace Forces (Rosgvardiya) arrived in Belarus.
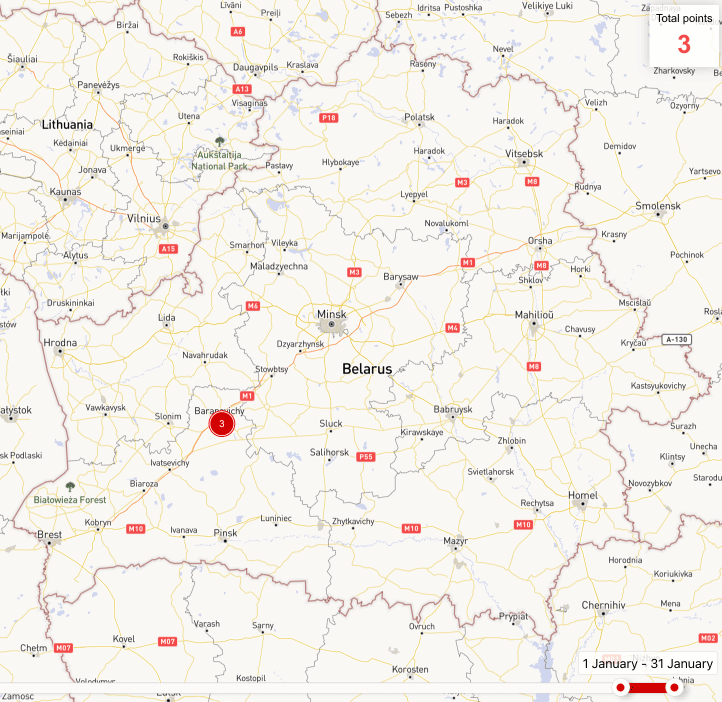
Also, on January 17, 26 and 30, flights of fighters of the Russian Aerospace Forces were recorded at Baranavichy airfield.
We received no information on the changes in the number of the Russian Aerospace Forces aviation group during the month. As of February 1, the following aircraft of the Russian Aerospace Forces are permanently stationed on the territory of Belarus:
- at Lida airfield – one Su-25 attack aircraft;
- at Baranavichy airfield – two Su-24M/MR aircraft and at least one Su-30SM fighter.
The media spread information that there’ve allegedly been more than 60 aircraft and helicopters of the Russian Aerospace Forces in Belarus. However, this information was incorrectly presented: the total number included aircraft and helicopters of the Belarusian Air Force.
3. Wagner private military company
The situation with mercenaries in Belarus didn’t change compared to the previous months.
The mercenaries continue to conduct systematic trainings with servicemen of the Internal Troops. Deeper cooperation with the Belarusian Armed Forces was also reported (for more details, see paragraph 1.1 of the review).
As for the current number of the mercenaries in Belarus, we can note the following. One of the Telegram channels related to the mercenaries reported at the end of January that there were “more than 300 instructors in several training centers working in Belarus to this day.” Previously, we estimated the number of mercenaries in Belarus at several hundred people.
No active movements of PMC Wagner mercenaries on the territory of Belarus have been recorded.
Speaking of the prospects for the presence of the mercenaries in Belarus, we can note that the forecasts described in the review for October remain valid.
4. General conclusions
1) In January, intensive combat training continued in the Belarusian Armed Forces, which is typical in the beginning of the academic year in the troops. During the month, a number of units were subject to various inspections. Some units were at training grounds, where they were engaged in combat training and unit coordination.
Speaking of combat training, we can note that the Belarusian Armed Forces intensively use the experience of the war in Ukraine. This was demonstrated, for example, in the manufacture and use of anti-drone canopies on military equipment, intensive use of various types of UAVs in combat training, practicing methods of countering UAVs, etc.
At the same time, comparing the intensity of combat training of the Belarusian Armed Forces at the beginning of last year, we can note a decrease in its intensity. This is primarily connected with the withdrawal of the bulk of the Russian military contingent.
We should note that due to the “Steadfast Defender 2024” drills from January to May 2024, we can expect the Ministry of Defense of Belarus to respond. For example, by conducting additional combat readiness inspections or drills in the western regions of Belarus.
2) The general conclusion about the status of the Russian Armed Forces on the territory of Belarus didn’t change. The deployed units of the Russian troops don’t pose a threat to Ukraine and other countries bordering Belarus. At the moment, the number of the Russian contingent in Belarus may increase, for example, if a new wave of mobilization in Russia is announced, or under the influence of other unpredictable events.
An illustrative indicator of the low activity of the Russian Armed Forces in Belarus is the absence of arrivals of military transport and passenger aircraft of the Russian Aerospace Forces in January. We note that arrivals of aircraft are often related to the delivery of military cargo or personnel for rotations. It is also remarkable that aircraft didn’t arrive in Belarus for the first time since February 2022.
Currently, one of the factors that could potentially affect the increase of the Russian military presence in Belarus is the ratification of the agreement on the establishment and functioning of the joint combat training centers. So far, there has been no public announcement of the establishment of these structures on the territory of Belarus. There should be no illusions: if the training centers are established in Belarus, soldiers and military equipment of the Russian Armed Forces will be stationed there.
In general, the level of activity of the Russian Armed Forces in Belarus in January can be described as very low.
3) All conclusions regarding the prospects for the deployment of PMC Wagner mercenaries in Belarus given in the review for October 2023 remain valid. A small number of mercenaries are still stationed in Belarus, who serve as instructors for law enforcement agencies. An important change of the last month has been the beginning (or restoration?) of closer cooperation between the mercenaries and the Belarusian Armed Forces.
In general, the level of activity of PMC Wagner in Belarus in December can be described as low.
